Hetzel, M., Lopez-Rodriguez, E., Mucci, A., Nguyen, A.H.H., Suzuki, T., Shima, K., Buchegger, T., Dettmer, S., Rodt, T., Bankstahl, J.P., Malik, P., Knudsen, L., Schambach, A., Hansen, G., Trapnell, B.C., Lachmann, N., Moritz, T.: Haematologica. 2020;105(4):1147-57.
To access the full article, click here:

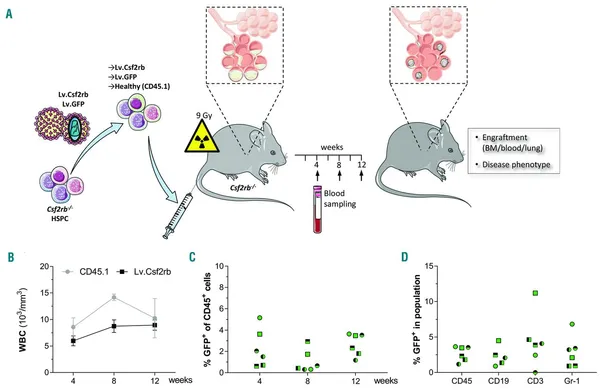
Hereditary pulmonary alveolar proteinosis due to GM-CSF receptor deficiency (herPAP) constitutes a life-threatening lung disease characterized by alveolar deposition of surfactant protein secondary to defective alveolar macrophage function. As current therapeutic options are primarily symptomatic, we have explored the potential of hematopoietic stem cell-based gene therapy. Using Csf2rb−/− mice, a model closely reflecting the human herPAP disease phenotype, we here demonstrate robust pulmonary engraftment of an alveolar macrophage population following intravenous transplantation of lentivirally corrected hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Engraftment was associated with marked improvement of critical herPAP disease parameters, including bronchoalveolar fluid protein, cholesterol and cytokine levels, pulmonary density on computed tomography scans, pulmonary deposition of Periodic Acid-Schiff+ material as well as respiratory mechanics. These effects were stable for at least nine months. With respect to engraftment and alveolar macrophage differentiation kinetics, we demonstrate the rapid development of CD11c+/SiglecF+ cells in the lungs from a CD11c–/SiglecF+ progenitor population within four weeks after transplantation. Based on these data, we suggest hematopoietic stem cell-based gene therapy as an effective and cause-directed treatment approach for herPAP.